How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and essential controls to advanced flight modes and legal considerations. We’ll explore various drone types and their unique capabilities, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the skies.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering both the technical aspects of flight and the responsible practices needed for safe and legal operation. This guide will walk you through the necessary steps, helping you develop proficiency in handling a drone, understanding its features, and respecting relevant regulations. We will cover a range of topics, from basic controls to advanced techniques, ensuring a well-rounded understanding of drone operation.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting key components, assessing environmental conditions, and understanding potential hazards. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, equipment damage, and even injury.
Pre-flight Inspection and Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection covers several critical areas. This includes verifying battery charge levels, checking the integrity of propellers, and confirming a strong GPS signal. The following checklist provides a structured approach.
| Item | Check | Notes | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Charge | Sufficient charge (at least 80%) | Check battery indicator lights and voltage. | Replace if necessary; fully charge before next flight. |
| Propeller Integrity | Inspect for cracks, chips, or damage. | Ensure all propellers are securely attached. | Replace damaged propellers immediately. |
| GPS Signal Strength | Strong signal (at least 6 satellites) | Check GPS indicator on the controller or app. | Relocate to an area with better GPS reception if needed. |
| Gimbal Calibration | Verify gimbal is level and properly calibrated. | Perform calibration if necessary, following manufacturer’s instructions. | Recalibrate if needed. |
| Drone Body | Inspect for any damage or loose parts. | Check all connections and fasteners. | Tighten any loose parts. Report significant damage to manufacturer. |
| Flight Area | Clear airspace, no obstructions. | Check for power lines, trees, buildings, and people. | Choose an alternative location if necessary. |
Safe Launch and Landing Procedures
Launching and landing a drone safely requires consideration of environmental factors. Windy conditions and confined spaces present unique challenges that demand careful maneuvering.
- Windy Conditions: Launch and land into the wind to minimize drift. Maintain a firm grip on the controller and be prepared for gusts.
- Confined Spaces: Choose a spacious area with ample clearance. Practice slow and controlled movements, and be extra cautious of obstacles.
- General Procedure: Always perform a pre-flight check before launch. Begin with a slow, controlled ascent, and maintain visual contact with the drone throughout the flight. For landing, execute a slow, controlled descent, ensuring a smooth touchdown.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is vital for safe drone operation. Loss of signal and low battery situations require immediate action to prevent accidents.
- Loss of Signal: If signal is lost, most drones have a “Return to Home” (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If RTH fails, attempt to regain signal by moving closer to the drone’s last known location.
- Low Battery: Upon low battery warnings, immediately initiate a return to the launch point. Never push the drone to its absolute limit; prioritize a safe landing.
Drone Controls and Operation
Understanding drone controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. Different drones offer varying control methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Types of Drone Controls
Most drones use either joystick-based controllers or app-based controls via smartphones or tablets. Joystick controllers provide precise, tactile control, while app-based controls offer intuitive interfaces but may lack the precision of joysticks. The choice depends on personal preference and the specific drone model.
- Joystick Controllers: Offer greater precision and responsiveness, particularly in challenging conditions. They require a steeper learning curve.
- App-Based Controls: Provide a user-friendly interface, ideal for beginners. However, they can be less precise and responsive than joystick controllers, especially in windy conditions or during complex maneuvers.
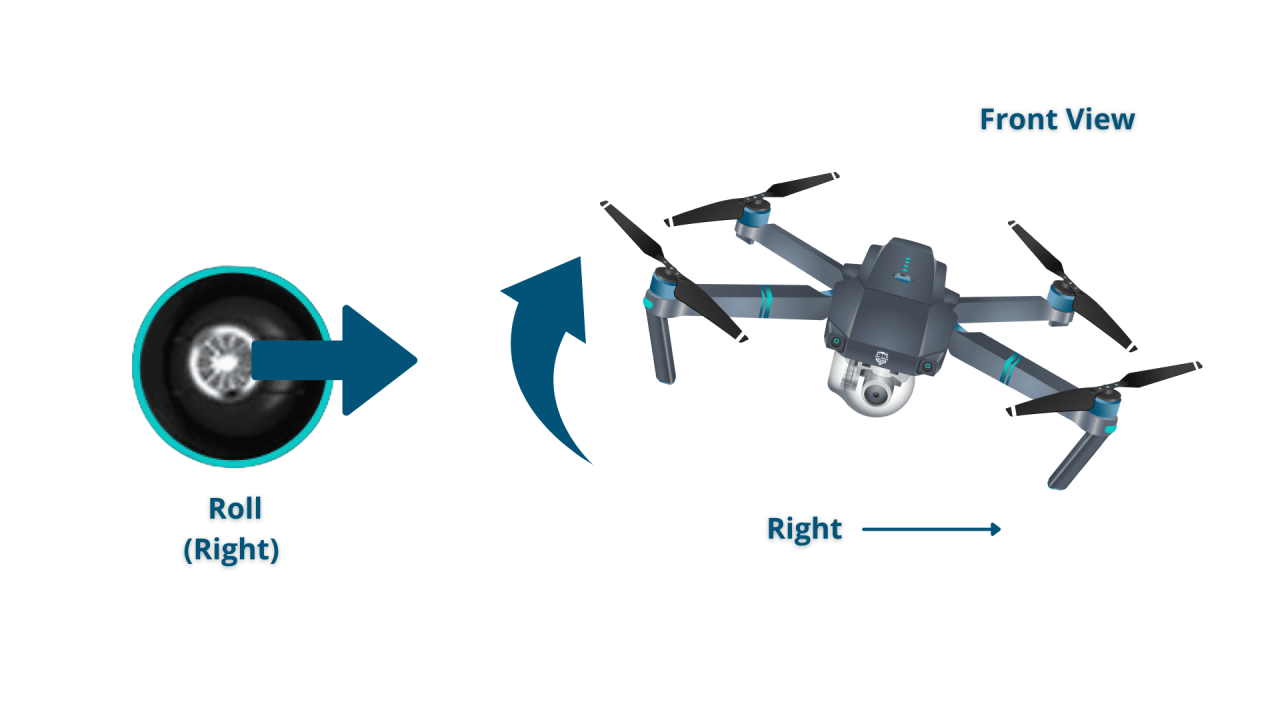
Drone Maneuvering Techniques
Mastering drone control involves understanding how joystick movements translate into drone actions. Precise control is essential for smooth, stable flights and high-quality aerial photography.
Consider this simplified representation of joystick control:
Left Stick:
Up: Forward
Down: Backward
Left: Left Strafe
Right: Right Strafe
Right Stick:
Up: Ascend
Down: Descend
Left: Yaw Left (Rotate Left)
Right: Yaw Right (Rotate Right)
Tips for Smooth and Precise Control
Smooth and precise drone control comes with practice. Here are some tips to improve your skills:
- Start Slow: Begin with gentle movements, gradually increasing speed and complexity as you gain confidence.
- Practice Hovering: Master hovering before attempting more complex maneuvers. This is crucial for stable shots.
- Use Trimming: Use the trimming functions to compensate for any drift or imbalance.
- Anticipate Wind: Account for wind conditions and adjust your movements accordingly.
Flight Modes and Features: How To Operate A Drone

Modern drones offer various flight modes and features that enhance safety, simplify operation, and improve image quality. Understanding these features is essential for maximizing your drone’s capabilities.
Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to varying skill levels and flight scenarios. Beginner mode limits speed and responsiveness, while sport mode allows for more aggressive maneuvers.
- Beginner Mode: Restricts speed and responsiveness, ideal for learning and practicing.
- Sport Mode: Enables faster speeds and more agile maneuvers, suitable for experienced pilots.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): Automatically returns the drone to its home point, useful in case of signal loss or low battery.
- Follow Me Mode: Drone automatically follows a designated subject.
- Waypoint Mode: Allows the drone to fly a pre-programmed route.
Drone Features and Functionalities, How to operate a drone
Key drone features significantly enhance functionality and usability. GPS enables precise positioning, while obstacle avoidance systems enhance safety.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, from pre-flight checks to maneuvering, is crucial. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from takeoff to landing, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and master the art of aerial photography. Safe and responsible drone operation ensures both your safety and the safety of others.
- GPS: Enables precise positioning and return-to-home functionality.
- Camera: Captures high-resolution photos and videos.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Helps prevent collisions with obstacles.
- Gimbal Stabilization: Provides smooth, stable footage even during flight maneuvers.
Comparison of Drone Models
Different drone models offer varying features and capabilities. The following table compares three fictional drone models.
| Feature | Drone A | Drone B | Drone C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Camera Resolution | 4K | 1080p | 4K |
| Flight Time | 30 minutes | 25 minutes | 35 minutes |
| Obstacle Avoidance | Yes | No | Yes |
| GPS | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Max Speed | 60 km/h | 50 km/h | 70 km/h |
Photography and Videography with Drones
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning aerial photography and videography. Mastering camera settings and composition techniques is crucial for creating compelling visuals.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Understanding camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture is vital for achieving optimal image quality. These settings influence brightness, sharpness, and depth of field.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity to light. Lower ISO values result in less noise but require more light.
- Shutter Speed: Determines how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds can create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera lens. A wider aperture (lower f-number) creates a shallower depth of field, blurring the background.
Composing Aerial Shots
Effective composition is crucial for visually appealing aerial shots. Consider the rule of thirds, leading lines, and framing techniques to create impactful images.
- Rule of Thirds: Position key elements along imaginary lines that divide the frame into thirds.
- Leading Lines: Use natural lines (roads, rivers) to draw the viewer’s eye into the scene.
- Framing: Use natural elements (trees, buildings) to frame your subject.
Capturing Smooth, Stable Footage
Smooth, stable footage is essential for professional-looking videos. Cinematic flight maneuvers can add visual interest, but require practice and precision.
- Slow Movements: Avoid jerky movements by making slow, deliberate adjustments.
- Gimbal Stabilization: Utilize the drone’s gimbal to minimize camera shake.
- Cinematic Flight Maneuvers: Practice smooth, controlled movements like orbiting and tracking shots.
Aerial Video Storyboard
A storyboard Artikels the shots and angles for a video project. Here’s a simple example:
Scene 1: Wide shot of a coastline at sunset. Camera slowly pans across the beach. (Drone at 50m altitude)
Scene 2: Close-up shot of surfers riding waves. Drone follows a surfer from behind, maintaining a steady distance. (Drone at 20m altitude)
Scene 3: High-angle shot of the surfers from above. Drone slowly circles the surfers. (Drone at 80m altitude)
Scene 4: Drone flies towards the beach, descending to reveal a group of people enjoying the sunset. (Drone descends from 50m to 10m)
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to legal regulations and ethical guidelines. These considerations are crucial for ensuring safe and respectful drone usage.
Drone Laws and Regulations
Drone operation is subject to various laws and regulations that vary by location. These regulations typically cover airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational limits.
(Note: This section requires specific legal information for a particular region. Consult local aviation authorities for up-to-date regulations.)
Ethical Considerations

Ethical drone usage emphasizes respecting privacy, personal space, and property rights. Responsible drone operation prioritizes safety and avoids intrusive or harmful actions.
- Privacy: Avoid filming people without their consent. Respect personal space and avoid intruding on private property.
- Safety: Always operate the drone safely and responsibly, avoiding collisions or endangering others.
- Property Rights: Obtain permission before flying over private property.
Responsible Drone Use in Populated Areas
Operating a drone in populated areas requires extra caution. Maintain awareness of your surroundings, and avoid flying near crowds or sensitive locations (hospitals, schools).
Best Practices for Ethical and Legal Drone Operation
- Register your drone as required by law.
- Always check local regulations before flying.
- Maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Respect the privacy of others.
- Fly responsibly and safely.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This ensures longevity, peak performance, and prevents unexpected issues.
Drone Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning and maintenance extend the life of your drone. This involves cleaning the drone body, inspecting propellers, and maintaining batteries.
- Cleaning the Drone Body: Use a soft cloth to wipe away dirt and debris. Avoid using harsh chemicals.
- Inspecting Propellers: Check for cracks, chips, or damage. Replace damaged propellers immediately.
- Battery Care: Store batteries in a cool, dry place. Avoid overcharging or discharging.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Understanding common drone problems and their solutions is vital for efficient troubleshooting.
| Problem | Potential Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Low Battery Warning | Low battery charge, high power consumption | Charge battery, reduce flight time, optimize drone settings. |
| GPS Signal Loss | Weak signal, interference, obstructions | Relocate to an area with better GPS reception, check for obstructions. |
| Motor Malfunctions | Motor damage, loose connections | Inspect motors for damage, check connections, contact manufacturer for repair. |
| Drone Not Responding | Low battery, signal interference, controller issues | Check battery level, move to a location with less interference, check controller batteries and connections. |
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is vital for extending the life of your drone and maintaining its performance. It prevents potential problems and ensures safe and reliable operation.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of technical skill, responsible practice, and a keen understanding of applicable regulations. By diligently following pre-flight procedures, practicing controlled maneuvers, and adhering to ethical guidelines, you can unlock the full potential of your drone while ensuring safety and compliance. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the best drone for beginners?
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires knowledge of regulations and safe flying practices. For a comprehensive guide on the intricacies of piloting, including practical tips and safety protocols, please refer to this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, proficient drone operation demands consistent practice and a thorough understanding of your equipment and the surrounding environment.
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners. Look for features like GPS, obstacle avoidance, and return-to-home functionality.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and usage. Check the manufacturer’s specifications for an estimate. Always carry extra batteries.
What is the legal age to fly a drone?
Drone regulations vary by location. Check your local laws to determine the minimum age requirement and any licensing or registration needs.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and sometimes by drone weight. Check your local aviation authority’s website for details.